Demystifying Margin Trading: A Comprehensive Guide for Investors
Introduction:
What is Margin Trading ?
Margin trading is a financial strategy that allows investors to amplify their buying power in the financial markets. While it offers the potential for increased profits, it also comes with higher risks. In this blog, we’ll delve into the concept of margin trading, its mechanics, and the associated risks and rewards.Open free demat account
Understanding Margin Trading:
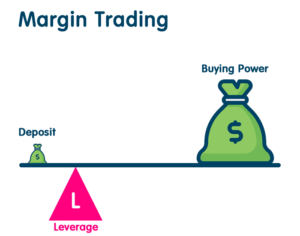
Margin trading involves borrowing funds to increase the size of a trading position beyond what one could afford with their own capital alone. In traditional trading, investors use their own money to buy securities, but in margin trading, they can borrow money from a broker to increase their investment capacity.
How Margin Trading Works:
- Margin Account: To engage in margin trading, investors need to open a margin account with a brokerage. This account allows them to borrow funds against the value of their existing securities.
- Leverage: Leverage is the key feature of margin trading. What is Margin Trading ? It magnifies both potential gains and losses. For example, if an investor has $1,000 and uses 2x leverage, they can control a position worth $2,000.
- Margin Call: Brokers set a minimum account balance, known as the maintenance margin. If the value of securities falls below this level due to market movements, What is Margin Trading ? the broker may issue a margin call, requiring the investor to deposit additional funds or sell some securities to cover losses.
Pros of Margin Trading:
- Share valuation metrics,
- Financial analysis,
- Stock investment,
- Profitability ratios,
- Investor insights,
- Share market strategies,
- Income statement analysis,
- Corporate earnings evaluation.
- Increased Buying Power: Margin trading allows investors to control larger positions with a relatively smaller amount of capital.
- Potential for Higher Returns: With leverage, investors have the potential to earn higher returns on successful trades.What is Margin Trading ?
- Short Selling: Margin accounts enable investors to sell assets they don’t own (short selling), profiting from a decline in prices.
Risks of Margin Trading:
- Amplified Losses: While leverage magnifies gains, it also amplifies losses. A small adverse market movement can result in significant losses.
- Margin Calls: If the value of securities falls below the maintenance margin, investors may face margin calls,What is Margin Trading ? requiring them to deposit more funds or sell assets at potentially unfavorable prices.
- Interest Costs: Borrowed funds come with interest costs, which can eat into profits, especially if the trades are held for an extended period.Open free demat account
Risk Management in Margin Trading:
- Set Clear Limits: Establish predefined entry and exit points for trades to manage risk effectively.
- Diversification: Diversify your portfolio to spread risk across different assets and reduce the impact of a single investment’s poor performance.
- Stay Informed: Keep a close eye on market trends, news, and economic indicators to make informed decisions.
Conclusion:
Margin trading can be a powerful tool for experienced investors, but it’s not without risks. It demands a thorough understanding of market dynamics, risk management strategies,What is Margin Trading ? and financial discipline. What is Margin Trading ? Before engaging in margin trading, investors should carefully assess their risk tolerance, financial goals, and market knowledge to make informed and responsible decisions in the pursuit of financial success.


