Demystifying Day Trading: Understanding the Ins and Outs
Introduction:
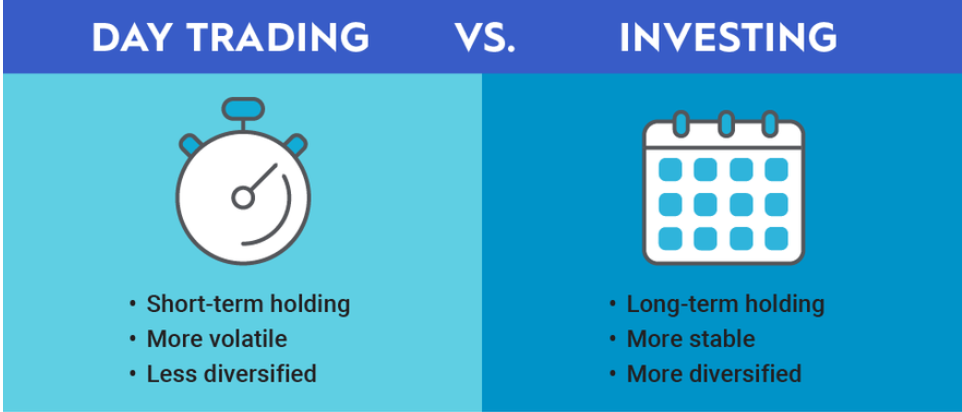
What is day trading? Day trading is a financial strategy that has gained popularity in recent years, drawing in individuals eager to capitalize on short-term market fluctuations. This form of trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day, aiming to profit from intraday price movements.What is day trading? In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of day trading, exploring its intricacies and shedding light on how it operates.
What is day trading?
Understanding Day Trading:
- Time Horizon: Day trading stands in stark contrast to long-term investment strategies. While traditional investors may hold onto assets for weeks, months, or even years, day traders open and close positions within the span of a single trading day.What is day trading? This short time horizon requires a keen understanding of market dynamics and the ability to make quick decisions.
- Financial Instruments: Day traders primarily engage in trading stocks, currencies (forex), options, and futures contracts. These instruments offer the liquidity and volatility necessary for intraday trading. What is day trading? OPEN FREE DEMAT ACCOUNT The choice of financial instruments depends on a trader’s preference, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
- Risk Management: Successful day trading relies heavily on effective risk management. Traders often employ strategies like setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Given the fast-paced nature of day trading, it’s crucial for traders to establish risk-reward ratios and adhere to strict risk management practices to protect their capital.
- Technical Analysis: Day traders heavily rely on technical analysis, utilizing charts, indicators, and patterns to make informed decisions. Technical analysis involves studying historical price data to identify trends, support and resistance levels, and potential entry and exit points. Common tools include moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands.
- Leverage: Day traders often use leverage to amplify their positions, allowing them to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. While leverage can enhance profits, it also magnifies losses.What is day trading? Traders must exercise caution and have a solid understanding of the risks associated with leverage.
How Day Trading Works:
- Market Entry: Day traders typically start their day by analyzing pre-market and early morning market conditions. Based on their analysis, they identify potential entry points for trades.
- Execution: Once a trade is planned, day traders execute orders swiftly, taking advantage of short-term price movements. The goal is to capitalize on small price changes and accumulate profits throughout the day.What is day trading?
- Monitoring and Adaptation: Constant monitoring of positions is crucial in day trading. Traders keep a close eye on market news, economic indicators, and other factors that may impact prices. They adapt their strategies as market conditions evolve throughout the trading day.
- Closing Positions: Day traders close their positions before the market closes to avoid overnight risks. Unpredictable events, such as earnings reports or geopolitical developments, can cause significant price gaps, impacting positions left open overnight.
Conclusion:
Day trading is a dynamic and challenging approach to financial markets that demands a combination of analytical skills, discipline, and risk management. While potential profits can be enticing, day trading is not without risks, and individuals considering this strategy should thoroughly educate themselves and, if possible, practice with simulated accounts before venturing into live markets. Successful day trading requires continuous learning, adaptability, and a resilient mindset in the face of market uncertainties.