Understanding Common Stock : A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
Common stock is a fundamental financial instrument that plays a crucial role in the world of investing and corporate finance. Whether you are a seasoned investor or just starting to dip your toes into the world of stocks, understanding common stock is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what common stock is, its characteristics, how it works, and the implications for investors.Open demat account
What is Common Stock?
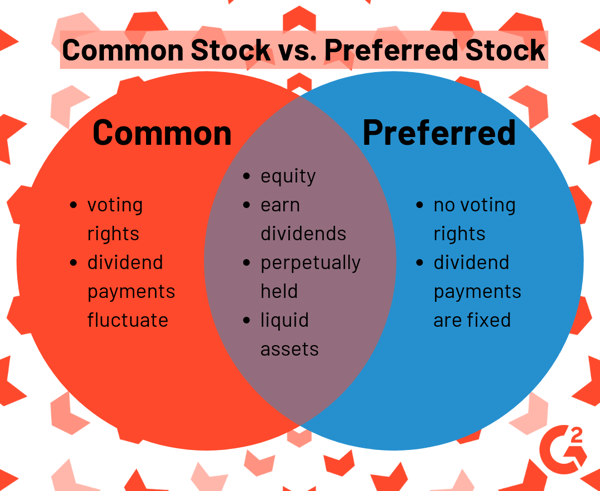
Common stock represents ownership in a corporation and signifies a claim on part of the company’s assets and earnings. When investors purchase common stock, they become shareholders, owning a portion of the company proportional to the number of shares they hold. Shareholders have the right to vote on certain corporate matters and may receive dividends if the company distributes profits.Open demat account
Key Characteristics of Common Stock:
- Ownership and Voting Rights:
- Shareholders have the right to vote on key decisions affecting the company, such as the election of the board of directors and major corporate policy changes.
- The number of votes typically corresponds to the number of shares owned, granting larger shareholders more influence.
- Dividends:
- Unlike preferred stockholders, common stockholders do not have a fixed dividend rate. Dividends are decided by the board of directors and are not guaranteed.
- Some companies may choose to reinvest profits into the business rather than distribute them as dividends.
- Residual Claim on Assets:
- In the event of liquidation or bankruptcy, common stockholders have a residual claim on the company’s assets after all debts and preferred stock obligations are settled.
- This means common stockholders are at a higher risk compared to bondholders and preferred stockholders.
- Price Volatility:
- Common stock prices are subject to market forces and can experience significant fluctuations based on company performance, industry trends, and broader economic conditions.
- Investors may profit from price appreciation or suffer losses depending on market movements.
Open freee demat account
How Common Stock Works:
- Issuance:
- Companies issue common stock through initial public offerings (IPOs) or subsequent stock offerings to raise capital for various purposes, such as expansion, research and development, or debt repayment.
- Market Trading:
- After the initial issuance, common stock is traded on stock exchanges, where investors can buy and sell shares. The price is determined by supply and demand dynamics.
- Investor Returns:
- Common stock investors can earn returns through two primary channels: capital appreciation (selling the stock at a higher price than purchased) and dividends (if the company distributes profits).
Implications for Investors:
- Risk and Reward:
- Common stock is considered a higher-risk investment due to its volatility, but it also offers the potential for significant returns.
- Investors must carefully assess their risk tolerance and investment goals before including common stocks in their portfolios.
- Research and Due Diligence:
- Successful investing in common stocks requires thorough research into the company’s financial health, management team, competitive position, and industry trends.
- Regular monitoring of the investment is essential to adapt to changing market conditions.
How the market Works? | All about stock market | Sky Stock Mart
What is the Meaning of Lots in stock market ?
is Stock market trading good for housewife ?
अपनी बेटी के विकास के लिए इन्वेस्टमेंट करे – SIP म्यूच्यूअल फण्ड में
Conclusion:
Common stock is a foundational element of the financial markets, providing investors with an opportunity to participate in the ownership and success of a company. While the potential for high returns exists, it comes with inherent risks. As with any investment, a well-informed approach, diversification, and a long-term perspective are key to navigating the dynamic world of common stocks successfully.


